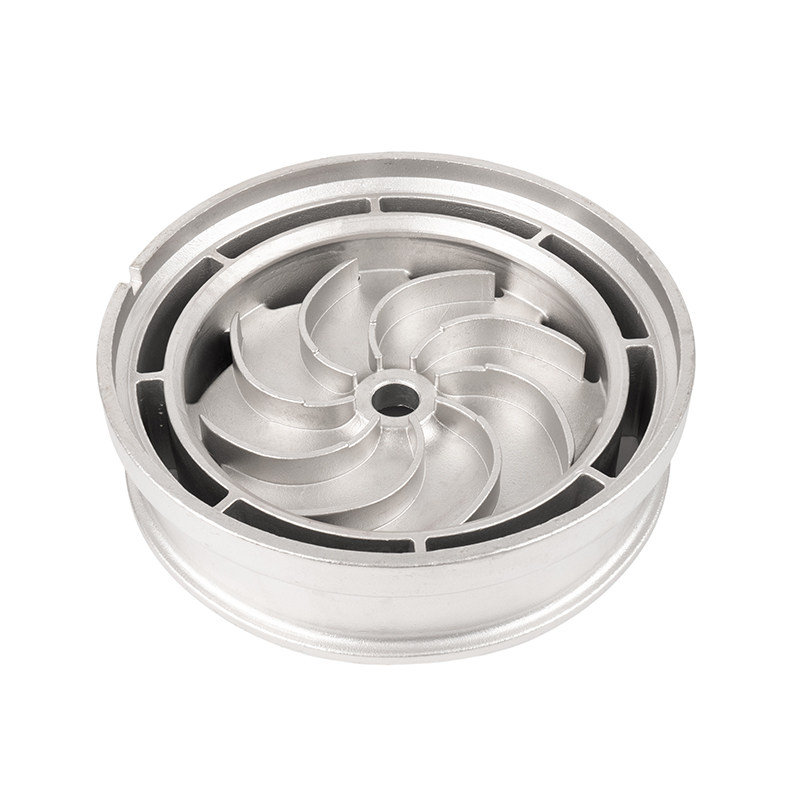
What are the common casting methods for stainless steel impellers
Stainless steel blade impeller casting is a critical process in high-precision machinery manufacturing. The choice of casting method directly affects impeller mechanical performance, corrosion resistance, and service life. Different casting techniques are suitable for varying impeller complexities, material requirements, and production volumes. Understanding common casting methods and their characteristics helps optimize production processes and improve product quality.
Sand Casting
Sand casting is one of the most traditional and widely used methods for stainless steel impeller production. A sand mold cavity is created in the shape of the impeller, and molten stainless steel is poured into the mold to solidify.
Sand casting is suitable for medium-to-large impellers, offering flexibility in design and low mold costs, making it ideal for complex geometries and small-to-medium production volumes. The surface finish is relatively rough, requiring post-casting machining. Optimizing sand materials, grain size, and venting systems can reduce porosity, inclusions, and shrinkage defects, improving overall casting quality.
Investment Casting (Precision Casting)
Investment casting, also known as lost-wax casting, is a key method for producing high-precision stainless steel impellers. Wax models are coated with ceramic shells, molten stainless steel is poured into the shells, and the ceramic is removed after solidification.
This method is suitable for thin blades, complex structures, and components requiring high dimensional accuracy. Investment casting achieves excellent surface finish and reduces post-machining requirements. Strict control of metal flow, pouring temperature, and shell thickness helps minimize segregation, shrinkage, and inclusions, enhancing mechanical performance and corrosion resistance.
Centrifugal Casting
Centrifugal casting utilizes rotational centrifugal force to distribute molten stainless steel evenly along the mold wall. It is particularly effective for hub and disc-type impellers.
This method significantly improves casting density and mechanical properties while reducing porosity and inclusion concentration. Controlling rotation speed, pouring temperature, and cooling rate optimizes grain structure and reduces segregation risk. Centrifugal casting enhances impact toughness and fatigue life, making it ideal for structural components subjected to high stress.
Die Casting
Die casting is suitable for small, high-precision stainless steel impellers. Molten metal is injected under high pressure into metal molds and rapidly cooled to form the casting.
Die casting offers high production efficiency, excellent dimensional accuracy, and smooth surface finish, ideal for large-scale production. Careful control of alloy composition and mold design is necessary to accommodate metal shrinkage and optimize flow paths. This method effectively reduces surface defects and internal porosity, ensuring consistent impeller performance.
Continuous Casting
Continuous casting involves solidifying molten stainless steel into semi-finished forms through water-cooled or air-cooled molds, which are subsequently machined into impellers.
It is suitable for large impellers and high-performance alloys, allowing control over grain structure, minimizing segregation, and improving mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. Continuous casting requires precise control of melting temperature, solidification rate, and mold cooling, making it ideal for industrial-scale mass production.
Refining and Melting Integration
Casting stainless steel impellers also relies on proper refining and melting techniques. Electric furnace melting, vacuum induction melting, and ladle refining control chemical composition and reduce inclusions, ensuring uniform internal structure and enhancing corrosion resistance and fatigue strength. The integration of refining processes with casting methods is crucial for high-quality impeller production.


 English
English Español
Español русский
русский 中文简体
中文简体